#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int a[3][3],b[3][3],c[3][3],i,j;
printf("Enter the First matrix->");
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
printf("\nEnter the Second matrix->");
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
scanf("%d",&b[i][j]);
printf("\nThe First matrix is\n");
for(i=0;i<3;i++){
printf("\n");
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
printf("%d\t",a[i][j]);
}
printf("\nThe Second matrix is\n");
for(i=0;i<3;i++){
printf("\n");
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
printf("%d\t",b[i][j]);
}
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
c[i][j]=a[i][j]-b[i][j];
printf("\nThe Subtraction of two matrix is\n");
for(i=0;i<3;i++){
printf("\n");
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
printf("%d\t",c[i][j]);
}
return 0;
}
Subtraction of two matrixes:
Rule: Subtraction of two matrixes is only possible if both matrixes are of same size.
Suppose two matrixes A and B is of same size m X n
Subtraction of two marixes is defined as
(A - B)ij = Aij - Bij
Where 1 ≤ i ≤ m and 1 ≤ j ≤ n
For example:
Suppose two matrixes A and B of size of 3 X 2 is as follow:

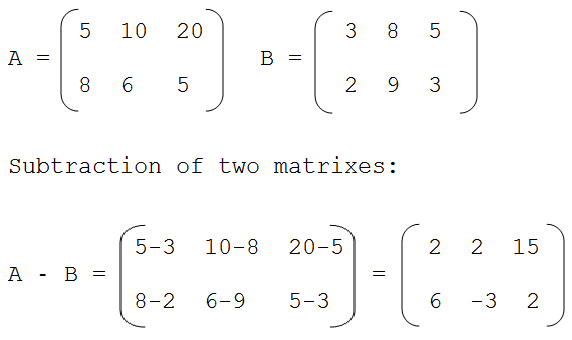

No comments:
Post a Comment